This post describes three examples of installing /re-installing NuGet packages:
- Re-install a NuGet package manually
- Install NuGet packages from NuGet, via a PowerShell script
- Install NuGet packages from a local artifact feed, via a PowerShell script & Visual Studio
1.) Re-install a NuGet package manually
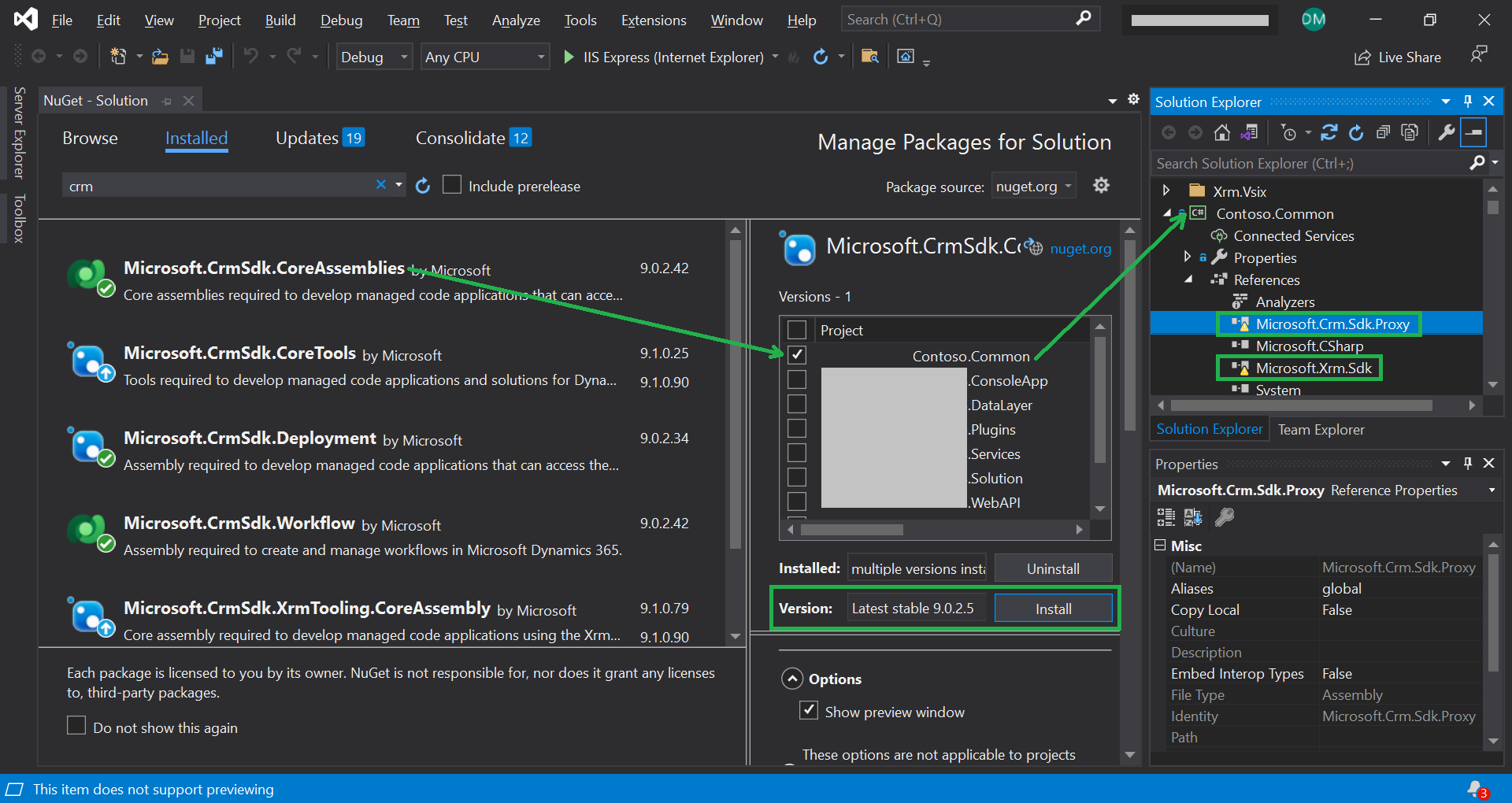
a.) Confirm that the NuGet package to be re-installed, exists in nuget.org (Figure 1)

b.) Setup Visual Studio so that it can connect to nuget.org

c.) Determine which version of the package is required to be re-installed by viewing packages.config

d.) Manually install the package
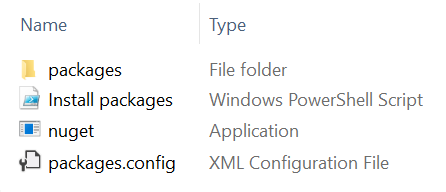
e.) Confirm that the missing package now exists in the packages folder i.e. …
- \packages\Microsoft.CrmSdk.CoreAssemblies.9.0.2.5\Microsoft.CrmSdk.CoreAssemblies.9.0.2.5.nupkg
Note: the assemblies are contained within the following folder
- \packages\Microsoft.CrmSdk.CoreAssemblies.9.0.2.5\lib\net462\Microsoft.Crm.Sdk.Proxy.dll & Microsoft.Xrm.Sdk.dll
2.) Install NuGet packages via a PowerShell script
a.) Connect to NuGet
Packages can also be downloaded from NuGet by executing the following PowerShell script (called ‘Install packages.ps1’)
$sourceNugetExe = "https://dist.nuget.org/win-x86-commandline/latest/nuget.exe"
$targetNugetExe = ".\nuget.exe"
if((Test-Path -Path $targetNugetExe) -eq $false)
{
Invoke-WebRequest $sourceNugetExe -OutFile $targetNugetExe
}
Set-Alias nuget $targetNugetExe -Scope Global
./nuget restore packages.config -PackagesDirectory packagesThe script downloads nuget.exe if it doesn’t already exist on the file system. It then downloads any packages that are listed in packages.config
b.) Connect to a local artifact feed
Packages can also be created, stored and downloaded from a local Artifact feed.
In this example:
- the local Artifact feed contoso-common-packages contains the NuGet package contosoCmdlets

The location of the Artifact feed is displayed in Figure 7
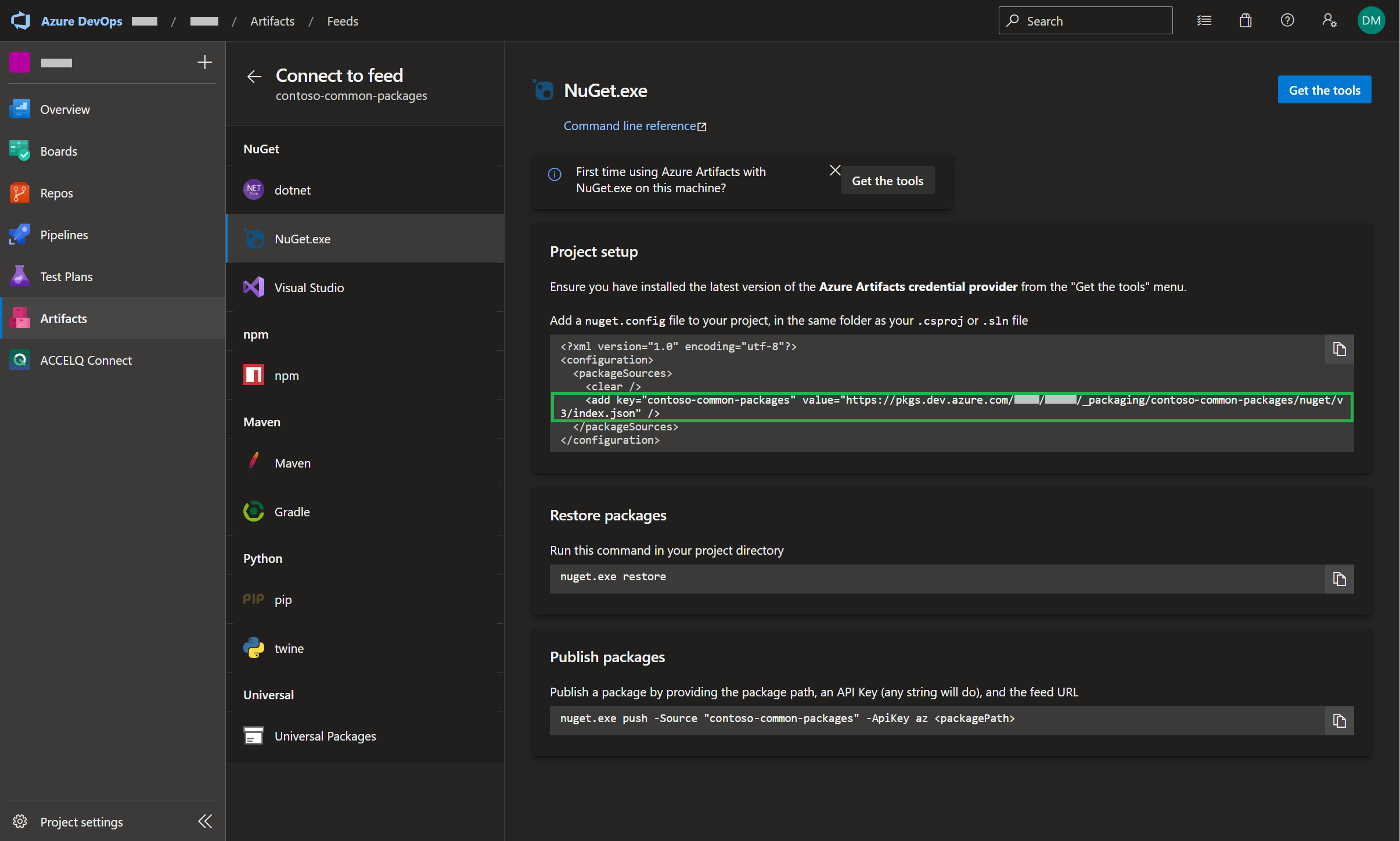
- this NuGet package can be downloaded by executing the following PowerShell script ‘Install Contoso Tools.ps1’
$version = "0.0.1.13";
$sourceNugetExe = "https://dist.nuget.org/win-x86-commandline/latest/nuget.exe"
$targetNugetExe = ".\nuget.exe"
if((Test-Path -Path $targetNugetExe) -eq $false)
{
Write-Host "Invoke-WebRequest $sourceNugetExe -OutFile $targetNugetExe"
Invoke-WebRequest $sourceNugetExe -OutFile $targetNugetExe
}
Set-Alias nuget $targetNugetExe -Scope Global
Write-Host "./nuget install ContosoCmdlets -Version $version -Source https://pkgs.dev.azure.com/.../_packaging/contoso-common-packages/nuget/v3/index.json -OutputDirectory ./packages"
./nuget install ContosoCmdlets -Version $version -Source https://pkgs.dev.azure.com/.../_packaging/contoso-common-packages/nuget/v3/index.json -OutputDirectory ./packages- the NuGet package can also be downloaded in Visual Studio. This can be achieved by adding the artifact feed contoso-common-packages as a ‘Package Sources’ in the ‘NuGet Package Manager’. That is, by adding another Package Source as shown in Figure 8

Further reading
Create an Azure pipeline to build a Dynamics 365 based solution